Wisconsin Republicans revive income tax cut after Evers vetoed similar plan
Republican lawmakers called for tapping the state's projected $4 billion budget surplus to lower one income tax bracket from 5.3% to 4.4% and exclude the first $150,000 of a couple's retirement income from taxes.
Associated Press
August 29, 2023
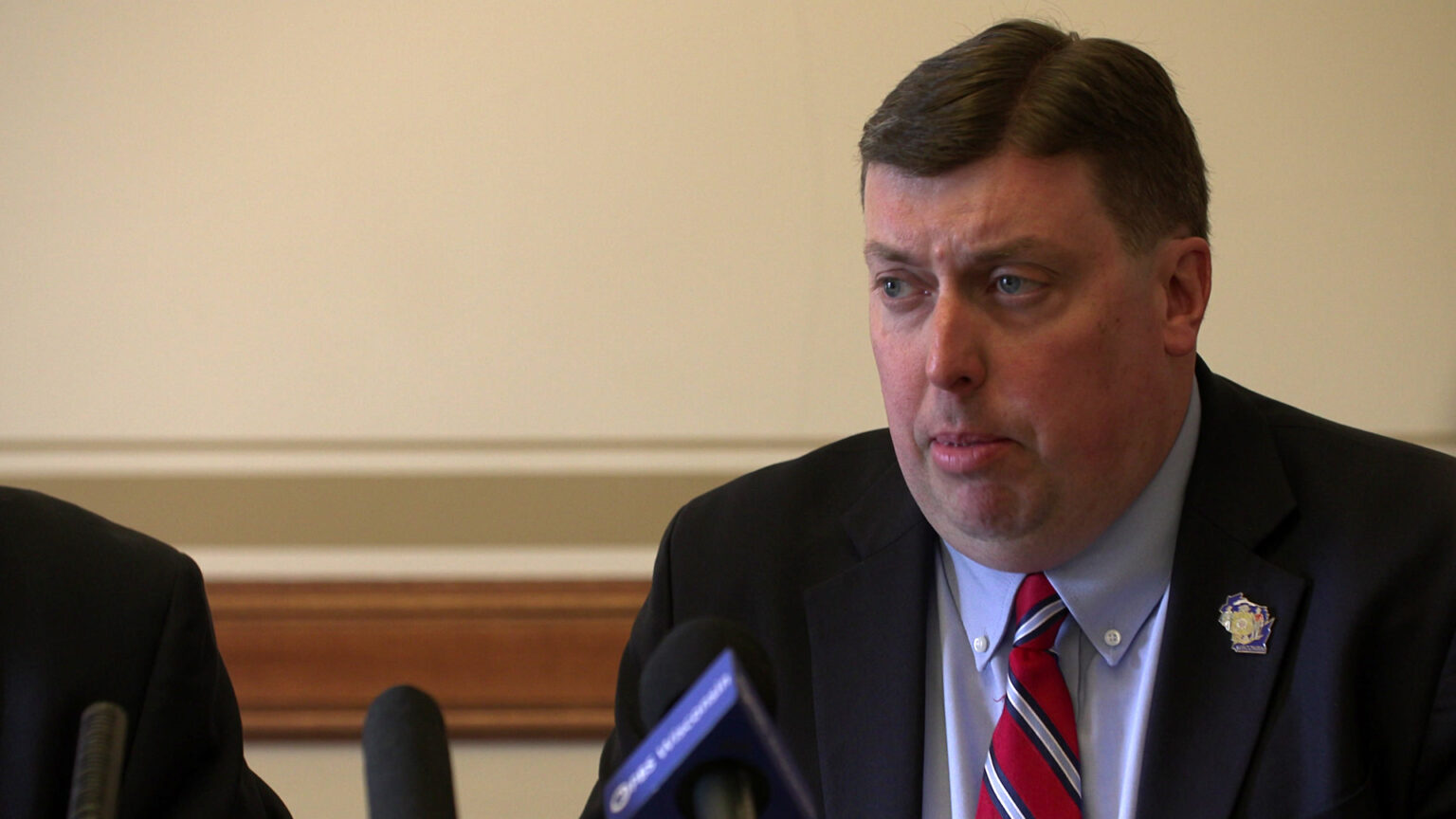

State Rep. Mark Born, R-Beaver Dam, speaks at a press conference on May 23, 2023, at the Wisconsin State Capitol in Madison. On Aug. 29, Born and other Republican legislators announced a $3 billion state income tax cut proposal. (Credit: PBS Wisconsin)

MADISON, Wis. (AP) — Wisconsin Assembly Republicans on Aug. 29 proposed a nearly $3 billion tax cut targeting the middle class, but it’s unclear whether Democratic Gov. Tony Evers is on board after he vetoed a similar tax cut in July.
“We’re giving the governor a second chance to do the right thing,” Rep. Mark Born, co-chair of the Legislature’s budget-writing committee, said at a news conference announcing the plan.
Republicans called for tapping the state’s projected $4 billion budget surplus to pay for the tax cut, which would lower the state’s third income tax bracket from 5.3% to 4.4% and exclude the first $150,000 of a couple’s retirement income from taxes. That would apply to people over age 67.
The income tax cut would mean that taxes for income between $27,630 and $304,170 for individuals, and between $36,840 and $405,550 for married couples, would drop from 5.3% to 4.4%. Every joint filer earning between $18,420 and $405,550 would be taxed at the same 4.4% rate.
Evers vetoed that same income tax cut in the state budget. He had no immediate comment on the new Republican proposal, but his spokesperson Britt Cudaback posted reminders on social media that Republicans had rejected a 10% middle class income tax cut the governor previously proposed.
The retirement tax cut is a new proposal. It would exempt the first $100,000 from an individual’s retirement income from taxes and the first $150,000 from a couple’s income. Under current law, money withdrawn from an individual retirement account, 401(k) plan or other retirement savings accounts are subject to Wisconsin income tax.
Evers has said he was open to reconsidering cutting taxes if Republicans would look at funding some of his priorities. Evers called a special session for the Legislature to spend more than $1 billion for child care, the University of Wisconsin System, worker shortage programs and other areas.
But Republicans have said they aren’t going to do that, a point Born repeated on Aug. 29.
“The Legislature is not interested in spending more money,” he said.
But Republicans are trying to work with Evers as evidenced by them not reviving the income tax cut for the highest bracket, which Evers also vetoed in July.
“We’re not trying to do the same thing,” Born said. “We’re trying to find a way to return this money to taxpayers.”
It was unclear whether Republicans in the Senate, which must also sign off on any tax cut, agree to the plan. Senate Majority Leader Devin LeMahieu did not commit to supporting the plan in a statement, saying only that the plan would be discussed as Republicans look for ways to cut taxes.
Sen. Rachael Cabral-Guevara is co-sponsoring the tax cut bill and attended the news conference. She said Republican senators want to cut taxes and they will discuss the proposal.
The Assembly was moving ahead quickly with the plan, scheduling a public hearing for Aug. 30. The full Assembly could vote on passing it as soon as mid-September.
Republicans also introduced a proposed constitutional amendment that would require a two-thirds vote to approve any tax increase. That measure would have to pass two consecutive legislative sessions and be approved by a vote of the people before taking effect.
The Assembly GOP tax cut plan comes after Evers vetoed a $3.5 billion income tax cut to just $175 million, which left the average taxpayer with a $3 monthly reduction in taxes. Evers argued then that he was vetoing the tax cut to make money available for other priorities.
Evers’ budget director issued a memo on Aug. 28 warning that cutting taxes more than $432 million over the next two years could jeopardize about $2.5 billion in federal pandemic relief money the state has received. But Born dismissed that concern, calling it a threat from the Evers administration that won’t happen.
But the nonpartisan Legislative Fiscal Bureau reported in June that it was unclear whether the recoupment provision of the law was enforceable. The bureau, which advises the Legislature on budget issues, noted that the 11th U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals affirmed a lower court’s ruling barring enforcement of that provision in 13 states and the U.S. Supreme Court is considering whether to review another case challenging the recoupment provision.
 Passport
Passport






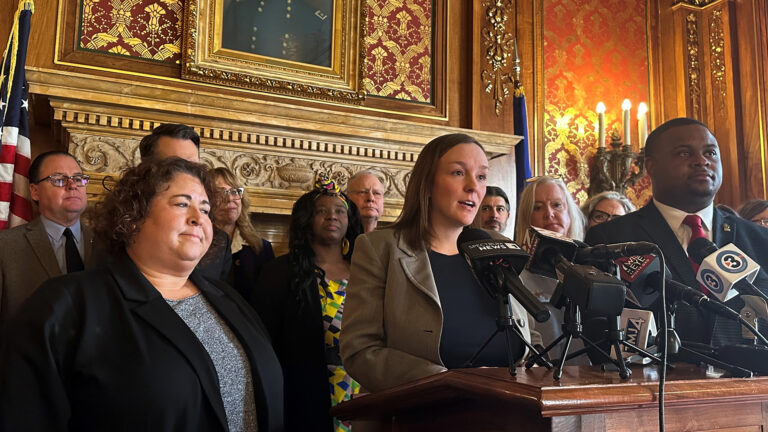



Follow Us