Starting Seeds Indoors Jumpstarts The Growing Season
Growing vegetables from seeds started indoors can be fun and rewarding.
April 16, 2018

Eggplant seedlings grown indoors in container

Growing vegetables from seeds started indoors can be fun and rewarding. Indoor seed starting is fairly simple and an inexpensive project that offers the advantage of choosing from a wide variety of seeds that may not be commonly available as transplants from garden centers.
The process of growing garden plants from seeds in containers requires attention to several important elements necessary to ensure success, including the materials that are needed, when seeds are best started, how they should be sown, where indoors containers can be placed, how to care for germinated seedlings and preparing the plants for moving outdoors.
Materials
- Gardeners should choose good quality seeds from reputable seed companies, as low quality seeds or those stored for more than five years can result in poor germination. They should select varieties that can mature within 110 growing days and give preference to disease-resistant characteristics.
- For seed starting, clean containers that are at least two inches deep with sufficient drainage holes can be used. Appropriate types of containers include plastic flats, trays, peat pots, egg cartons, plastic cups or cell packs. Previously used containers should be disinfected using 10 percent bleach solution, rinsed with clean water and allowed to air dry.
- A soilless mix containing peat and perlite/vermiculite is an ideal media for seed starting. Soilless media is light, sterile, well drained and holds enough moisture for seeds to germinate. Garden soil or potting soil should not be used, as it can contain weed seeds and plant pathogens, while the heaviness of those media can slow the germination process.
- A clear plastic dome or plastic cover that fit over the containers/trays can be beneficial for seed germination. It can retain heat and humidity in the media and spur the germination process. Once the seedlings germinate, the dome should be removed.
- All seedlings need bright light for successful growth. Lack of light can hinder germination, and cause skinny and elongated stems. Two 40-watt fluorescent bulbs, one warm white and one cool white, should be positioned six inches above the tray. As the seedlings start to grow, the bulbs’ height should be adjusted to maintain a six inch clearance above the plants. A timer can be used to set the light bulb duration from 12 to 16 hours per day.
Timing
Timing is critical when it comes to sowing seeds indoors. and it should be calculated based on optimum outdoor transplanting time. Sowing seeds too early can result in weak, spindly plants, while seeding too late can delay the maturity of the plants. Most vegetable crops need a head start of 4-8 weeks when germinated indoors, and will need to reach a minimum of 6 inches growth before being transplanted outside.
Sowing
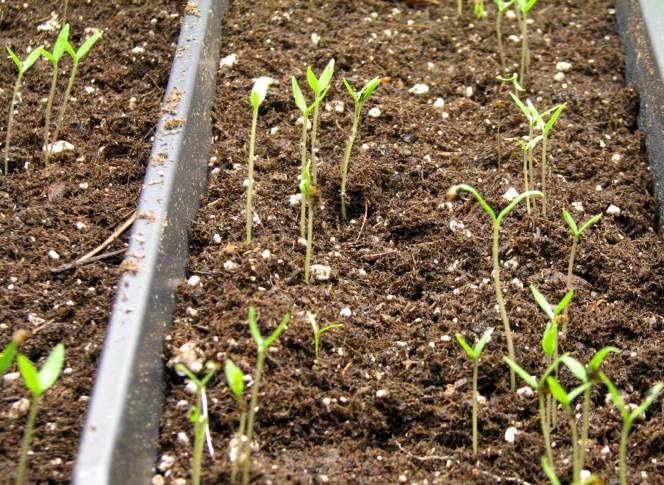
Just before sowing seeds, the container should be filled with pre-moistened soilless media and gently leveled. The seeds should be sown to the recommended depth listed on the seed packet.
Typically, large seeds are sown in pairs in a container to a depth of two or three times the diameter of the seed. The seeding hole should be covered lightly with surrounding media and pressed down gently. After the germination, the extra seedlings can be thinned by severing their stems at the media base.
Medium-sized seeds are best sown in furrows. An index finger or tool like a pencil can be used to make a shallow furrow across the surface of the growing media to a quarter inch deep, leaving a spacing of 1-2 inches between the rows. The seeds should be sown thinly and uniformly in the furrow and covered lightly with the growing medium.
Small, fine seeds should be sprinkled on the top of the growing media and dusted with soilless mix to thinly cover them.
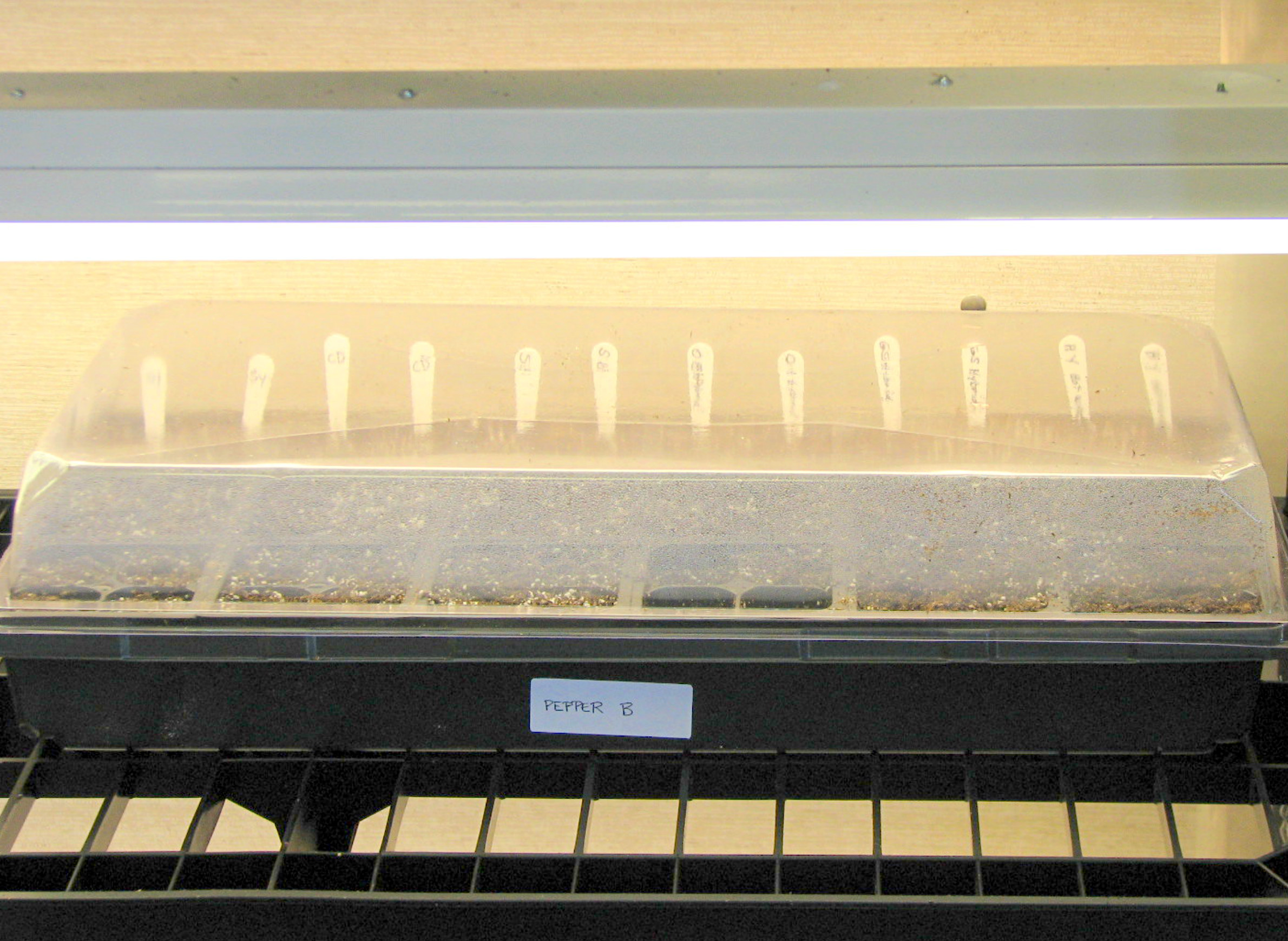

After the seeds are sown, the medium should be kept moist, but not wet. A fine mist sprayer can be used, or the container can be placed in a tray containing one inch of water. The container should be covered with a clear plastic dome or plastic wrap to hold the humidity. The container should be labeled with variety/cultivar name and the date of sowing. The dome or plastic cover should be removed for few minutes each morning to remove excess condensation and allow aeration.
Location
The seeded container should be placed in a warm location with a temperature of 65-75° F. It should not be placed in direct sunlight. Placing a heat pad underneath the tray can spur quicker germination and promote faster root formation. This practice can be beneficial for slow germinating seeds like peppers and eggplants. After the seedlings emerge, the cover and the heat pad should be removed.
Germinated seedlings care
The germinated seedling container should be kept in a ventilated location with the temperature of 65-70° F during the day and 60-65° F at night. Young seedlings require bright light and sufficient moisture. The fluorescent bulbs’ height should be adjusted to maintain a clearance of six inches above the seedlings. Moisture in the media should be checked daily and water added to the container from below when it starts to dry. If plants have been seeded in individual cell packs, the seedlings should be transplanted to a large container after they reach 4-6 inches high.
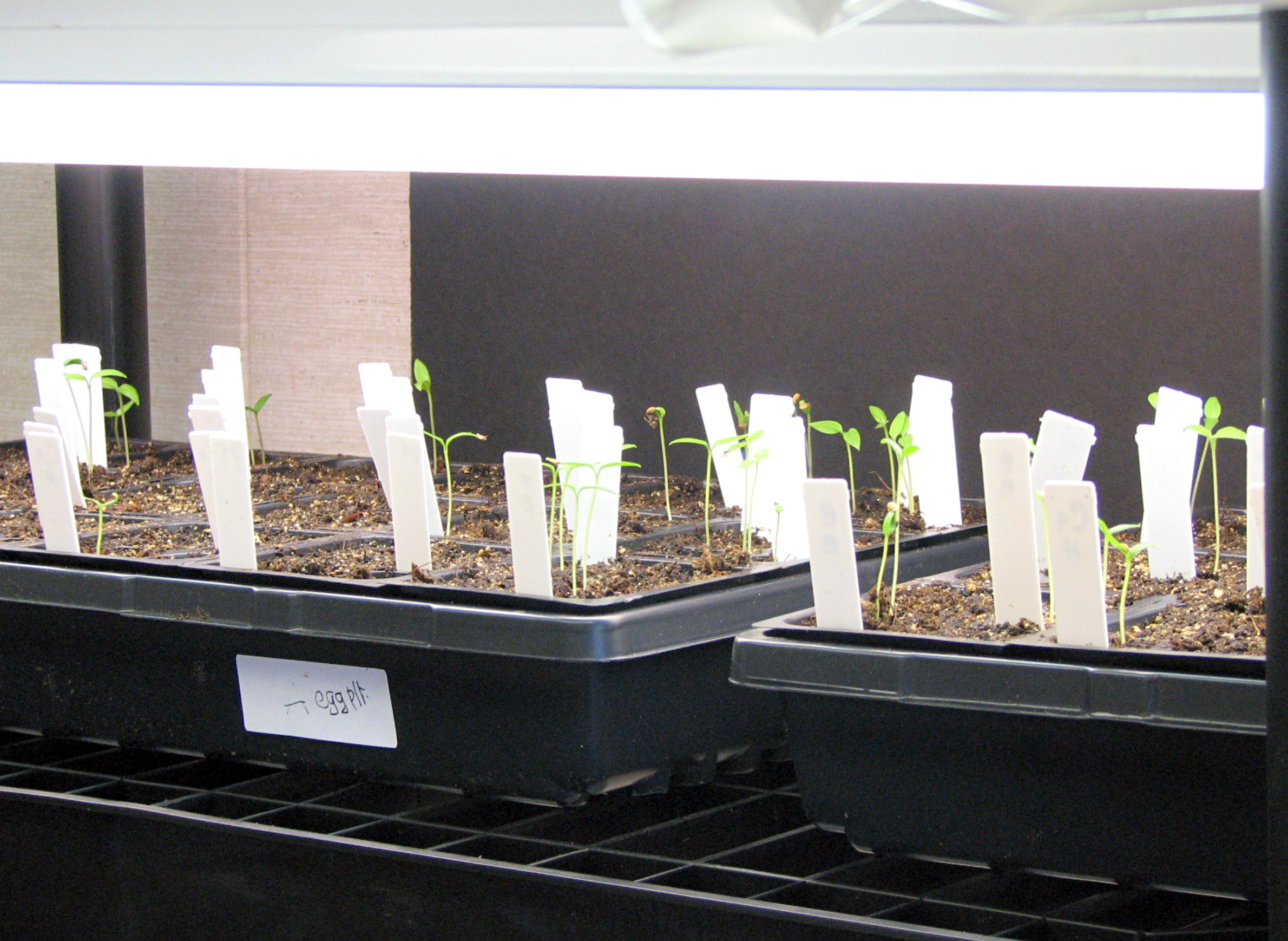

After the emergence of 4-5 sets of true leaves, the seedlings should be treated with water-soluble based fertilizer at one-quarter to one-half strength. Additional fertilizer should be applied weekly until the seedlings are transplanted outdoors. Brushing the seedlings lightly, or blowing on them with an oscillating fan set on low will toughen and prepare the seedlings for outdoor conditions.
Hardening
It is important to harden the plant to get it acclimatized to outdoor conditions. The hardening process should begin 7-10 days before transplanting outdoors. For first few days, the seedlings should be placed outside in a shaded area during day time and brought back indoors overnight.
After 3-4 days, the seedlings can be placed outside in the sheltered area all night. If the temperature drops below 60° F, a floating row cover or thin blanket should be used to protect the young plants. In case of frost, the plants should be brought indoors or placed in a cold frame.
After 6-7 days, the seedlings should be placed in a sunny area for couple of days before planting in ground. The seedlings should be watered and fertilized as needed during the hardening process.
Vijai Pandian is a horticultural agent and educator for the University of Wisconsin-Extension Brown County. This article is adapted from an item originally published by the Green Bay Press Gazette.
 Passport
Passport










Follow Us